Generate Any Excel Formula With AI
Use Sourcetable's AI assistant to create and understand complex Excel formulas. No advanced Excel skills required. Sign up to get started for free.

Trusted by students and professors at
Excel Formulas Made Easy With AI
Sourcetable leverages ChatGPT's powerful AI to help you create, understand, and optimize Excel formulas with ease.
Natural Language Formula Creation
Describe what you want to achieve in plain English, and AI will generate the appropriate Excel formula for you.
Try for free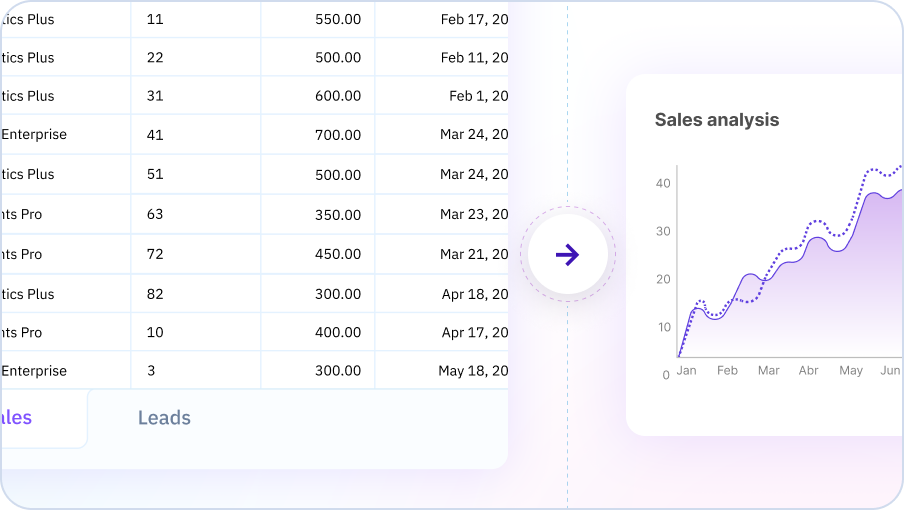
Formula Explanation
Get clear, step-by-step explanations of complex formulas, helping you understand and modify them with confidence.
Try for free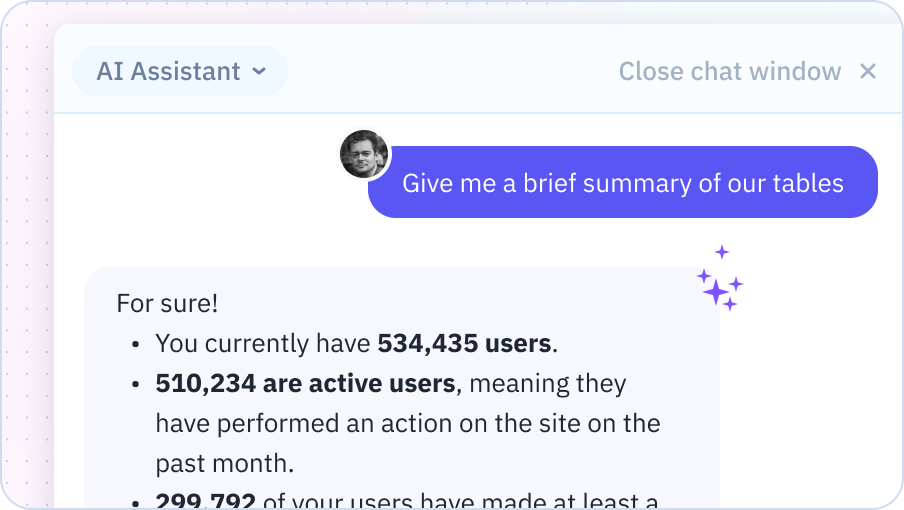
Formula Optimization
AI analyzes your formulas and suggests optimizations for better performance and readability.
Try for free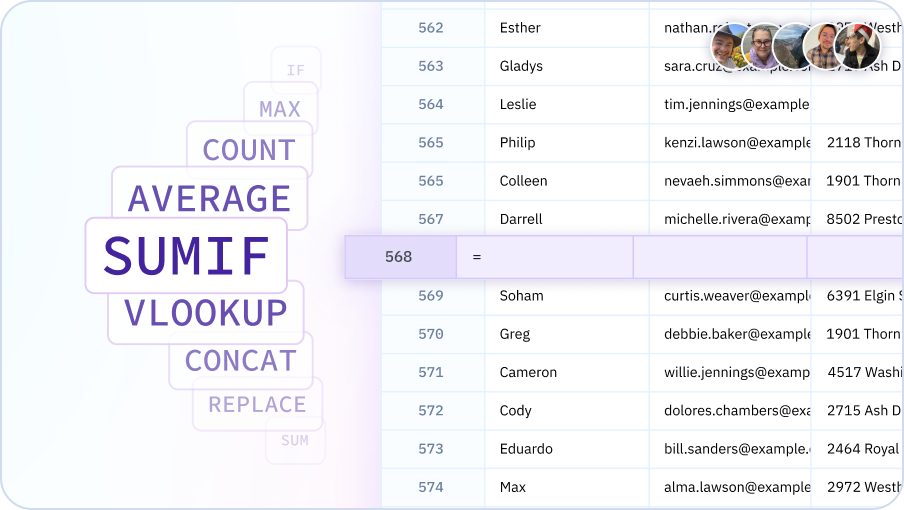
Error Detection and Correction
AI identifies errors in your formulas and provides suggestions to fix them, saving you time and frustration.
Try for free
AI tools to make you work smarter
Create spreadsheets from scratch. Generate and analyze your data. All with AI.

Sign Up For Free
Start creating powerful Excel formulas with AI. Sign up for Sourcetable today.

Team Purple
See what people are saying about Sourcetable's AI Excel Formula Assistant

Chris Aubuchon
@ChrisAubuchon
Spreadsheets are still the best interface for so many real world projects, it's time for @SourcetableApp to give them a reboot

Micah Alpern
@malpern
Love seeing innovation in this space after so many decades with very little.